You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.DetectCorners_CornerResponse Method
AVL.DetectCorners_CornerResponse Method
Detects corners using corner response method.
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void DetectCorners_CornerResponse( AvlNet.Image inMonoImage, AvlNet.Region inRoi, AvlNet.CornerResponseMethod inCornerResponseMethod, int inKernelSize, float? inThreshold, out AvlNet.Point2D[] outCorners, out AvlNet.Image outCornerResponseImage )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | inMonoImage | AvlNet.Image | Input image. | ||
 | inRoi | AvlNet.Region | Range of pixels to be processed. Default value: atl::NIL, or null. | ||
 | inCornerResponseMethod | AvlNet.CornerResponseMethod | Method for computing corner response. | ||
 | inKernelSize | int | <1, 10> | 3 | Method kernel size. Default value: 3. |
 | inThreshold | float? | <0.0f, 255.0f> | 50.0f | Threshold for corner response value, between 0 and 255, default value is taken from SelectThresholdValue on outCornerResponseImage and entropy method. Default value: 50.0f, or null. |
 | outCorners | AvlNet.Point2D | Found corner points | ||
 | outCornerResponseImage | AvlNet.Image |
Description
The operation detects corners using either Harris or Kanade-Tomasi corner response method,
depending on inCornerResponseMethod.
For every square window of size inKernelSize a convolution matrix is computed:
\[M = \left(\begin{array}{ccc}
\sum g_r^2 & \sum g_c g_r \\
\sum g_c g_r & \sum g_c^2
\end{array} \right) \]
where the summation is performed over the whole window
and \(g_r, g_c\) denote horizontal and vertical gradient respectively at the point.
Harris' corner response is computed the following way:
\[H = \mathrm{det}(M) - k \mathrm{tr}^2(M) \]
where k is a constant set to 0.01.
Kanade-Tomasi corner response is given by:
\[KT = \mathrm{min}(\lambda_1, \lambda_2)\]
where \(\lambda_1, \lambda_2\) are eigenvalues of the convolution matrix.
Values H or KT give corner response image.
Then a few steps are performed in order to extract corner points. First, the normalized corner response function is thresholded with inThreshold with a small hysteresis, then the remained points are split into connected regions (blobs) and the center of each blob is determined.
Examples
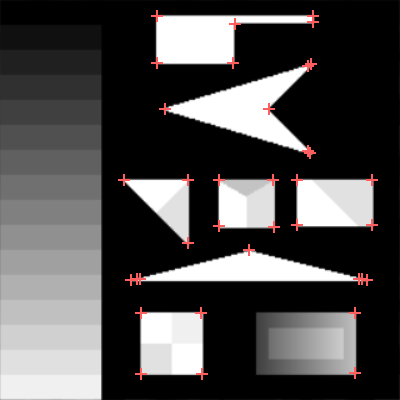 |
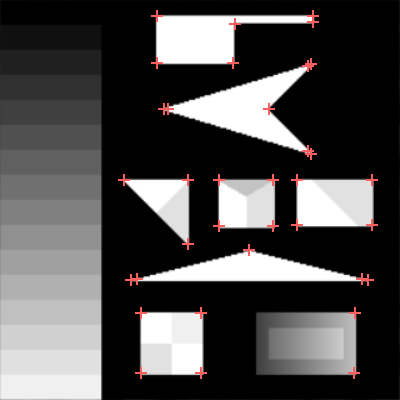 |
DetectCorners_CornerResponse with inThreshold=50, methods Harris and Kanade-Tomasi respectively.
Remarks
Both methods give similar results and are quite fast. However, they tend to be less accurate than DetectCorners_Foerstner.
Errors
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Unknown algorithm in DetectCorners_CornerResponse. |

