You are here: Start » Geometry 2D » Geometry 2D Angle Metrics » AngleBetweenSegments
AngleBetweenSegments
| Header: | AVL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | avl |
Measures the angle between two segments with one of four possible metrics.
Syntax
void avl::AngleBetweenSegments ( const avl::Segment2D& inSegment1, const avl::Segment2D& inSegment2, avl::AngleMetric::Type inAngleMetric, bool inAutodetectOrientation, atl::Optional<float&> outAbsoluteAngle = atl::NIL, atl::Optional<float&> outDirectedAngle = atl::NIL, atl::Optional<avl::Arc2D&> outArc = atl::NIL )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inSegment1 | const Segment2D& | First segment | |
 |
inSegment2 | const Segment2D& | Second segment | |
 |
inAngleMetric | AngleMetric::Type | Chooses one of four possible ways of measuring the angle | |
 |
inAutodetectOrientation | bool | True | Autodetects orientation of the segments assuming that these are two consecutive sides of a polygon |
 |
outAbsoluteAngle | Optional<float&> | NIL | Angle value used for measurements <0; 360> |
 |
outDirectedAngle | Optional<float&> | NIL | Angle value used for clockwise transformations <-360; 360> |
 |
outArc | Optional<Arc2D&> | NIL | Angle visualization object |
Optional Outputs
The computation of following outputs can be switched off by passing value atl::NIL to these parameters: outAbsoluteAngle, outDirectedAngle, outArc.
Read more about Optional Outputs.
Description
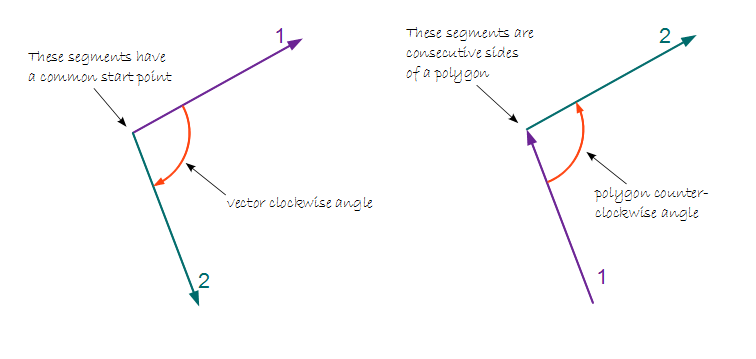
Angle between segments can be interpreted in two different ways:
- Segments as vectors - the angle is measured from the first to the second vector clockwise or counter-clockwise.
- Segments as consecutive sides of a polygon - the angle is measured from the first to the second side clockwise or counter-clockwise.
The method that is appropriate in a particular case can be chosen with the inAngleMetric input. Possible values are:
- VectorClockwiseAngle
- VectorCounterClockwiseAngle
- PolygonClockwiseAngle
- PolygonCounterClockwiseAngle
Segment Orientation
We do not usually care about orientation of a segment. However, when measuring angles, this information is important. In the most typical application, which is measuring an angle between two consecutive sides of a polygon, orientation of the segments is used together with inAngleMetric to determine the corner point and the side of the polygon (inside or outside). This information can also be obtained automatically by considering the intersection point between lines containing the segments. The inAutodetectOrientation parameter is there for that purpose. However, keep in mind that this method may produce unexpected results when the segments are parallel or nearly parallel.
Note that because of inaccuracies of floating-point arithmetic, some geometric operations (including this one) may lead to unpredictable results for degenerated cases. In this filter such a case occurs when an empty segment is given on input.
Examples
Errors
List of possible exceptions:
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Unsupported angle metric in AngleBetweenSegments. |
See Also
- AngleBetweenThreePoints – Measures the angle defined by three consecutive points.
- AngleBetweenVectors – Measures the angle between two vectors.

