You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.SplitRegionIntoBlobs(AvlNet.Region, AvlNet.RegionConnectivity, int, int?, bool, AvlNet.Region[])
AVL.SplitRegionIntoBlobs(AvlNet.Region, AvlNet.RegionConnectivity, int, int?, bool, AvlNet.Region[])
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void SplitRegionIntoBlobs( AvlNet.Region inRegion, AvlNet.RegionConnectivity inConnectivity, int inMinBlobArea, int? inMaxBlobArea, bool inRemoveBoundaryBlobs, out AvlNet.Region[] outBlobs )
Parameters
- inRegion
- Type: AvlNet.Region
- inConnectivity
- Type: AvlNet.RegionConnectivity
- inMinBlobArea
- Type: System.Int32
- inMaxBlobArea
- Type: System.Nullable<System.Int32>
- inRemoveBoundaryBlobs
- Type: System.Boolean
- outBlobs
- Type: AvlNet.Region
Description
The operation computes an array of connected regions corresponding to the connected components of the input region pixels. Each region in the resulting array will have dimensions equal to those of the input region.
Resulting array will contain only regions which have area in range defined by inputs: inMinBlobArea and inMaxBlobArea.
Images below shows neighbor of the gray pixel in different inConnectivity selection.
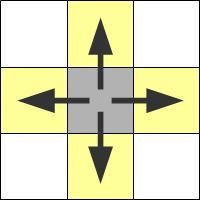 |
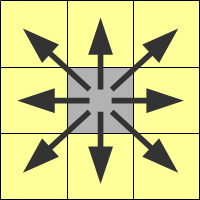 |
| inConnectivity.FourDirections | inConnectivity.EightDirections |
Examples
The image below show an input 10x10 pixels region.

Images below shows result of SplitRegionIntoBlobs filter with different inConnectivity.
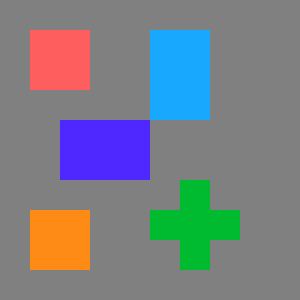 |
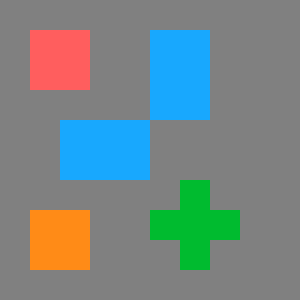 |
| inConnectivity.FourDirections | inConnectivity.EightDirections |
Images below shows result of SplitRegionIntoBlobs filter with different inRemoveBoundaryBlobs.
 |
 |
| inRemoveBoundaryBlobs = True | inRemoveBoundaryBlobs = False |
Remarks
When inRemoveBoundaryBlobs is set to True all filters near the region boundary will be removed. The region boundary is described by region frame.
This filter is mostly used in Blob Analysis Technique please refer to our Machine Vision Guide - Blob Analysis article.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Hardware acceleration settings may be manipulated with Settings class.


