You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.CloseRegion(AvlNet.Region, AvlNet.RegionMorphologyKernel, int, int?, AvlNet.Region)
AVL.CloseRegion(AvlNet.Region, AvlNet.RegionMorphologyKernel, int, int?, AvlNet.Region)
Performs a morphological closing on a region using selected predefined kernel.
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void CloseRegion( AvlNet.Region inRegion, AvlNet.RegionMorphologyKernel inKernel, int inRadiusX, int? inRadiusY, out AvlNet.Region outRegion )
Parameters
- inRegion
- Type: AvlNet.Region
Input region - inKernel
- Type: AvlNet.RegionMorphologyKernel
Kernel shape (predefined) - inRadiusX
- Type: System.Int32
Nearly half of the kernel's width (2*R+1) - inRadiusY
- Type: System.Nullable<System.Int32>
Nearly half of the kernel's height (2*R+1), or same as inRadiusX, or null. - outRegion
- Type: AvlNet.Region
Output region
Description
The operation performs a morphological closing, which is a tool used for filling gaps in a region. The operation is a convolution of two basic morphological operations:
- Firstly, the input region is dilated using DilateRegion operation.
- Then, the resulting region is eroded using ErodeRegion operation.
During the dilation gaps that are small enough are actually closed, while further erosion assures that the width of region limbs is preserved.
Both of the component operations are conducted using the same inKernel, inRadiusX and inRadiusY parameters.
Examples
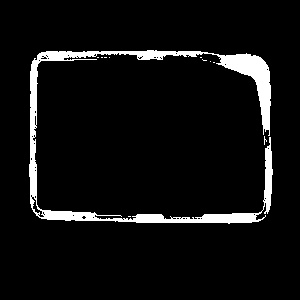 |
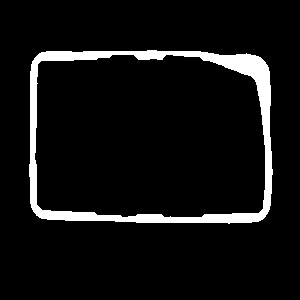 |
CloseRegion run with inKernel = Ellipse of dimensions inRadiusX = 5, inRadiusY = 5.
Errors
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Unsupported kernel in CloseRegion. |


