You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.ThresholdImage_Hysteresis(AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Region, float?, float?, float, AvlNet.Image)
AVL.ThresholdImage_Hysteresis(AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Region, float?, float?, float, AvlNet.Image)
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void ThresholdImage_Hysteresis( AvlNet.Image inImage, AvlNet.Region inRoi, float? inMinValue, float? inMaxValue, float inHysteresis, out AvlNet.Image outMonoImage )
Parameters
- inImage
- Type: AvlNet.Image
- inRoi
- Type: AvlNet.Region
- inMinValue
- Type: System.Nullable<System.Single>
- inMaxValue
- Type: System.Nullable<System.Single>
- inHysteresis
- Type: System.Single
- outMonoImage
- Type: AvlNet.Image
Description
The operation transforms each pixel value to the maximum or minimum level thus creating binary image. The result of the transformation depends on the pixel intensity:
- Pixel values in range [inMinValue, inMaxValue] are transformed to the maximum level.
- Pixel values lower than inMinValue-inHysteresis or higher than inMaxValue+inHysteresis are transformed to the minimum level.
- Pixel values in range [inMinValue-inHysteresis, inMinValue) or in range (inMaxValue, inMaxValue+inHysteresis] are transformed to the maximum if (and only if) in the processed image there is a path of consecutive pixels of value in range [inMinValue-inHysteresis, inMaxValue+inHysteresis] that connects the pixel being considered and any pixel with value in range [inMinValue, inMaxValue].
In the multichannel images the operation uses an average of channel values in each pixel, thus the resulting image is always monochromatic.
Examples
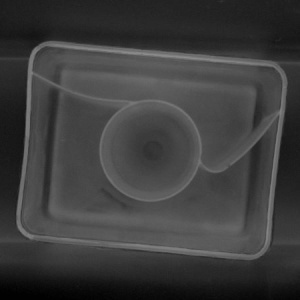 |
 |
ThresholdImage_Hysteresis performed on the sample image with inMinValue = 110.0, inMaxValue = Nil, inHysteresis = 15.0.
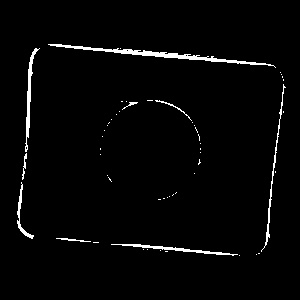 Pixels of the sample image brighter than 110.0. |
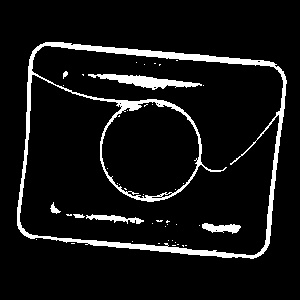 Pixels of the sample image brighter than 95.0. |
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Hardware acceleration settings may be manipulated with Settings class.


