You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.DetectMultipleCircles(AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Region, float, float, float, float, AvlNet.HoughCircle[], AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Image)
AVL.DetectMultipleCircles(AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Region, float, float, float, float, AvlNet.HoughCircle[], AvlNet.Image, AvlNet.Image)
Finds circles of a given radius in the input image.
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void DetectMultipleCircles( AvlNet.Image inImage, AvlNet.Region inRoi, float inRadius, float inMaxOverlap, float inMinScore, float inEdgeThreshold, out AvlNet.HoughCircle[] outCircles, out AvlNet.Image diagGradientMagnitudeImage, out AvlNet.Image diagScoreImage )
Parameters
- inImage
- Type: AvlNet.Image
Input image - inRoi
- Type: AvlNet.Region
Input region of interest, or null. - inRadius
- Type: System.Single
Circles' radius - inMaxOverlap
- Type: System.Single
Maximum accepted overlapping coefficient - inMinScore
- Type: System.Single
Minimum matching score - inEdgeThreshold
- Type: System.Single
Minimum accepted edge magnitude - outCircles
- Type: AvlNet.HoughCircle
Found circles - diagGradientMagnitudeImage
- Type: AvlNet.Image
Visualized gradients magnitude of an input image - diagScoreImage
- Type: AvlNet.Image
Calculated score for each pixel of an input image
Description
The operation detects circular objects of given radius (in pixels) in the inImage using the Hough Transform approach. The output array is ordered from best matching to worst matching results.
The parameter inMaxOverlap defines how much the detected circles can overlap. The value of 0 means no overlapping is allowed, and also that each circle must be fully contained in the search ROI, whereas the value of 1 allows full overlapping.
Examples
 |
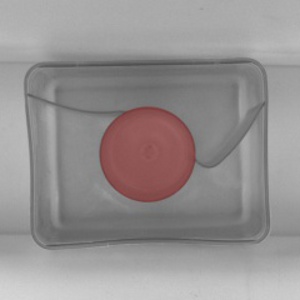 |
DetectMultipleCircles performed on the sample image.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Hardware acceleration settings may be manipulated with Settings class.


