You are here: Start » AVL.NET » AVL.ConvertToEquidistantPath(AvlNet.Path, float, AvlNet.EquidistanceType, AvlNet.Path)
AVL.ConvertToEquidistantPath(AvlNet.Path, float, AvlNet.EquidistanceType, AvlNet.Path)
Creates a new path whose characteristic points lie on the input path, but are equally spaced.
| Namespace: | AvlNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | AVL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void ConvertToEquidistantPath( AvlNet.Path inPath, float inStep, AvlNet.EquidistanceType inEquidistanceType, out AvlNet.Path outPath )
Parameters
- inPath
- Type: AvlNet.Path
Input path - inStep
- Type: System.Single
Requested distance between consecutive points - inEquidistanceType
- Type: AvlNet.EquidistanceType
Defines how the distance is measured - outPath
- Type: AvlNet.Path
Output path
Description
The operation follows a path from its beginning to the end, reselecting its characteristic points every inStep pixels. Note that this operation can significantly change the shape of a path, especially when the inStep value is relatively big.
To reduce the number of points in a path preserving its shape, one can use ReducePath filter.
Examples
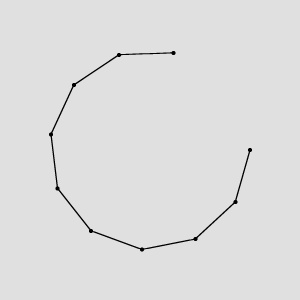 |
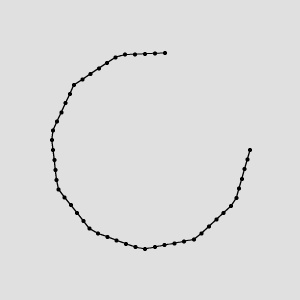 |
ConvertToEquidistantPath run on the sample path with inStep = 10 and inEquidistanceType = OutputPathEquidistance.
 |
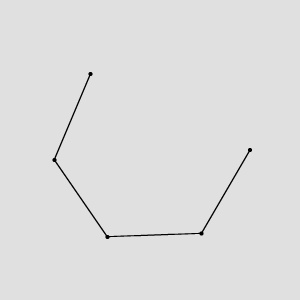 |
ConvertToEquidistantPath run on the sample path with inStep = 100 and inEquidistanceType = OutputPathEquidistance.
Errors
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | inStep has to be positive in ConvertToEquidistantPath. |


