You are here: Start » Filter Reference » Shape Features » ShapeOrientation
Computes the shape orientation as angle with value in range 0.0 - 180.0.
| Name | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
inShape | Path | |
 |
outOrientationAngle | Real |
Description
Shape orientation can be thought of as the direction in which the shape is oriented. Mathematically it is the angle between X-axis and the line passing through the shape mass center, that rotation around this line produces the smallest torque.
Note that if the input path is not a valid shape (i.e. it has at least one self-intersection), the computation may lead to results that are not intuitive.
Examples
 |
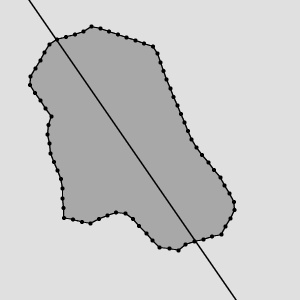 |
Orientation of the sample region equals to 55.386, which is visualized on the second image by drawing the line of this orientation passing through the mass center of the shape.
Errors
This filter can throw an exception to report error. Read how to deal with errors in Error Handling.
List of possible exceptions:
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Degenerate shape on input in ShapeOrientation. |
| DomainError | Open path on input in ShapeOrientation. |
Complexity Level
This filter is available on Basic Complexity Level.
See Also
- RegionOrientation – Computes the orientation of a region as an angle of value in range 0.0 - 180.0.


