You are here: Start » Filter Reference » 1D Edge Detection » ScanMultipleEdges
Locates multiple transitions between dark and bright pixels along a given path.
| Name | Type | Range | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inImage | Image | Input image to be measured | |
 |
inScanPath | Path | Path along which the scan is performed | |
 |
inScanPathAlignment | CoordinateSystem2D* | Adjusts the scan path to the position of the inspected object | |
 |
inScanWidth | Integer | 1 - 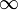 |
Width of the scan field in pixels |
 |
inImageInterpolation | InterpolationMethod | Interpolation method used in extraction of image pixel values | |
 |
inEdgeScanParams | EdgeScanParams | Parameters controlling the edge extraction process | |
 |
inMinDistance | Real | 0.0 - 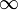 |
Minimal distance between consecutive edges |
 |
inMaxDistance | Real* | 0.0 - 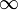 |
Maximal distance between consecutive edges |
 |
inLocalBlindness | LocalBlindness* | Defines conditions in which weaker edges can be detected in the vicinity of stronger edges | |
 |
outEdges | Edge1DArray | Found edges | |
 |
outGaps | Gap1DArray | Gaps between consecutive edges | |
 |
outAlignedScanPath | Path | Path along which the scan is performed; in the image coordinate system | |
 |
diagBrightnessProfile | Profile | Extracted image profile | |
 |
diagResponseProfile | Profile | Profile of the edge (derivative) operator response | |
 |
diagSamplingPoints | PathArray | Array of paths each one containing the sampling points that contributed to a single value of the extracted profile | |
 |
diagSamplingStep | Real | Used distance between consecutive sampling points on the scan path | |
Applications
Description
The operation scans the image along inScanPath and detects image edges perpendicular to the path. Depending on the inEdgeScanParams.edgeTransition parameter, edges representing increase or decrease (or both) of image brightness along the path will be taken into account.
When the number of edges to be found is known, one can use the ScanExactlyNEdges.
The optional parameter inScanPathAlignment defines a transform to be performed on the inScanPath so that the actual scan path (outAlignedScanPath) is adjusted to the position of the object, typically detected by one of Template Matching filters.
Note that in case of a scan path which is closed, the parameters controlling the distances between consecutive found objects do not control the distance between the first and the last of the found objects (counting from the beginning of the scan path).
Hints
- Connect an input image to the inImage input.
- Create inScanPath which is more or less perpendicular to the edges you want to detect. It should be long enough to anticipate all possible edge locations.
- Define inEdgeScanParams.EdgeTransition to detect a particular edge type, and only that type.
- Use a local coordinate system connected to inScanPathAlignment to automatically adjust the measurement to variable object position (optional).
- If the noise level is high, try increasing inScanWidth and/or inEdgeScanParams.SmoothingStdDev.
- If too few edges are found, try decreasing inEdgeScanParams.MinMagnitude. Verify this with the values on the diagResponseProfile output.
- If consecutive edges are closer than 6 pixels apart, change inEdgeScanParams.ProfileInterpolation to Quadratic3.
- Adjust inMinDistance (in pixels) to filter out false edges that appear in proximity to other edges.
Examples

ScanExactlyNEdges locates the edges across inScanPath.
Remarks
Read more about Local Coordinate Systems in Machine Vision Guide: Local Coordinate Systems.
This filter is a part of the 1D Edge Detection toolset. For a comprehensive introduction to this technique please refer to 1D Edge Detection and 1D Edge Detection - Subpixel Precision chapters of our Machine Vision Guide.
Complexity Level
This filter is available on Basic Complexity Level.
Filter Group
This filter is member of ScanEdges filter group.
See Also
- ScanSingleEdge – Locates the strongest transition between dark and bright pixels along a given path.
- ScanExactlyNEdges – Locates a specified number of the strongest transitions between dark and bright pixels along a given path.


