You are here: Start » Function Reference » 1D Edge Detection 3D » ScanExactlyNEdges3D
ScanExactlyNEdges3D
| Header: | AVL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | avl |
Locates a specified number of the strongest changes of surface height along a given path.
Syntax
void avl::ScanExactlyNEdges3D ( const avl::Surface& inSurface, const avl::ScanMap& inScanMap, const avl::EdgeScanParams3D& inEdgeScanParams, int inEdgeCount, avl::Selection::Type inEdgeSelection, float inMinDistance, atl::Optional<float> inMaxDistance, atl::Optional<const avl::LocalBlindness&> inLocalBlindness, atl::Optional<int> inMaxProfileGapWidth, atl::Conditional<atl::Array<avl::SurfaceEdge1D> >& outEdges, avl::Profile& diagHeightProfile, avl::Profile& diagResponseProfile )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inSurface | const Surface& | Input surface | ||
 |
inScanMap | const ScanMap& | Data precomputed with CreateSurfaceScanMap | ||
 |
inEdgeScanParams | const EdgeScanParams3D& | Parameters controlling the surface edge extraction process | ||
 |
inEdgeCount | int | 0 - 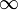 |
1 | Number of surface edges to be found |
 |
inEdgeSelection | Selection::Type | Selection::Best | Selection mode of the resulting edges | |
 |
inMinDistance | float | 0.0 - 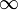 |
0.0f | Minimal distance between consecutive edges |
 |
inMaxDistance | Optional<float> | 0.0 - 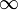 |
NIL | Maximal distance between consecutive edges |
 |
inLocalBlindness | Optional<const LocalBlindness&> | NIL | Defines conditions in which weaker edges can be detected in the vicinity of stronger edges | |
 |
inMaxProfileGapWidth | Optional<int> | 0 - 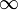 |
1 | Maximal number of consecutive not existing profile points |
 |
outEdges | Conditional<Array<SurfaceEdge1D> >& | Found surface edges | ||
 |
diagHeightProfile | Profile& | Extracted surface height profile | ||
 |
diagResponseProfile | Profile& | Profile of the edge (derivative) operator response |
Description
The operation scans the surface using inScanMap previously generated from a scan path and finds a set of inEdgeCount surface edges perpendicular to the path. If no subset (of inEdgeCount elements) of detected edges meets the requirements of inEdgeScanParams.minMagnitude, inMinDistance, inEdgeScanParams.edgeTransition then the outputs are set to NIL.
Note that in case of a scan path which is closed, the parameters controlling the distances between consecutive found objects do not control the distance between the first and the last of the found objects (counting from the beginning of the scan path).
The operation is very similar to ScanExactlyNEdges from 1D Edge Detection category, but there are some substantial differences. One of these is the possibility of absence of information, because some surface points may not exist at all. To detect such edges, where solely change of existence matters, Valid/Invalid options of inEdgeScanParams.EdgeTransition can be used. Outside the surface domain (i.e. rectangle defined by input surface width, height, offsets and scales) there are no valid or invalid points, so no edge can be found in the direct vicinity of the domain border.
Because in the Valid/Invalid mode all edges have equal strength, if inEdgeSelection is set to Best, it will be implicitly substituted with First selection option.
Please note that when the input surface has unequal scales along X and Y axes and the scan path is not parallel to any of the axes, the results may be slightly less accurate because of uneven sampling along axes.
Hints
- Set inEdgeCount to the number of edges that are to be found (the N number).
- Define inEdgeScanParams.EdgeTransition to detect a particular edge type, and only that type.
- If the expected number of edges cannot be found, try decreasing inEdgeScanParams.MinMagnitude. Verify this with the values on the diagResponseProfile output.
- If consecutive edges are closer than 6 pixels apart, change inEdgeScanParams.ProfileInterpolation to Quadratic3.
- Adjust inMinDistance (in surface coordinates) to filter out false edges that appear in proximity to other edges.
Remarks
Read more about Local Coordinate Systems in Machine Vision Guide: Local Coordinate Systems.
See Also
- CreateSurfaceScanMap – Precomputes a data object that is required for fast 1D edge detection in 3D.
- ScanSingleEdge3D – Locates the strongest change of surface height along a given path.
- ScanExactlyNEdges3D – Locates a specified number of the strongest changes of surface height along a given path.

